给定一个由 n 个元素组成的排序数组 arr[],编写一个函数来搜索 arr[] 中的给定元素 x。
一种简单的方法是进行线性搜索。上述算法的时间复杂度为 O(n)。执行相同任务的另一种方法是使用二分搜索。
二分搜索:通过重复将搜索间隔分成两半来搜索已排序的数组。从覆盖整个阵列的区间开始。如果搜索关键字的值小于区间中间的项,则将区间缩小到下半部分。否则,将其缩小到上半部分。反复检查直到找到值或间隔为空。
例子 :
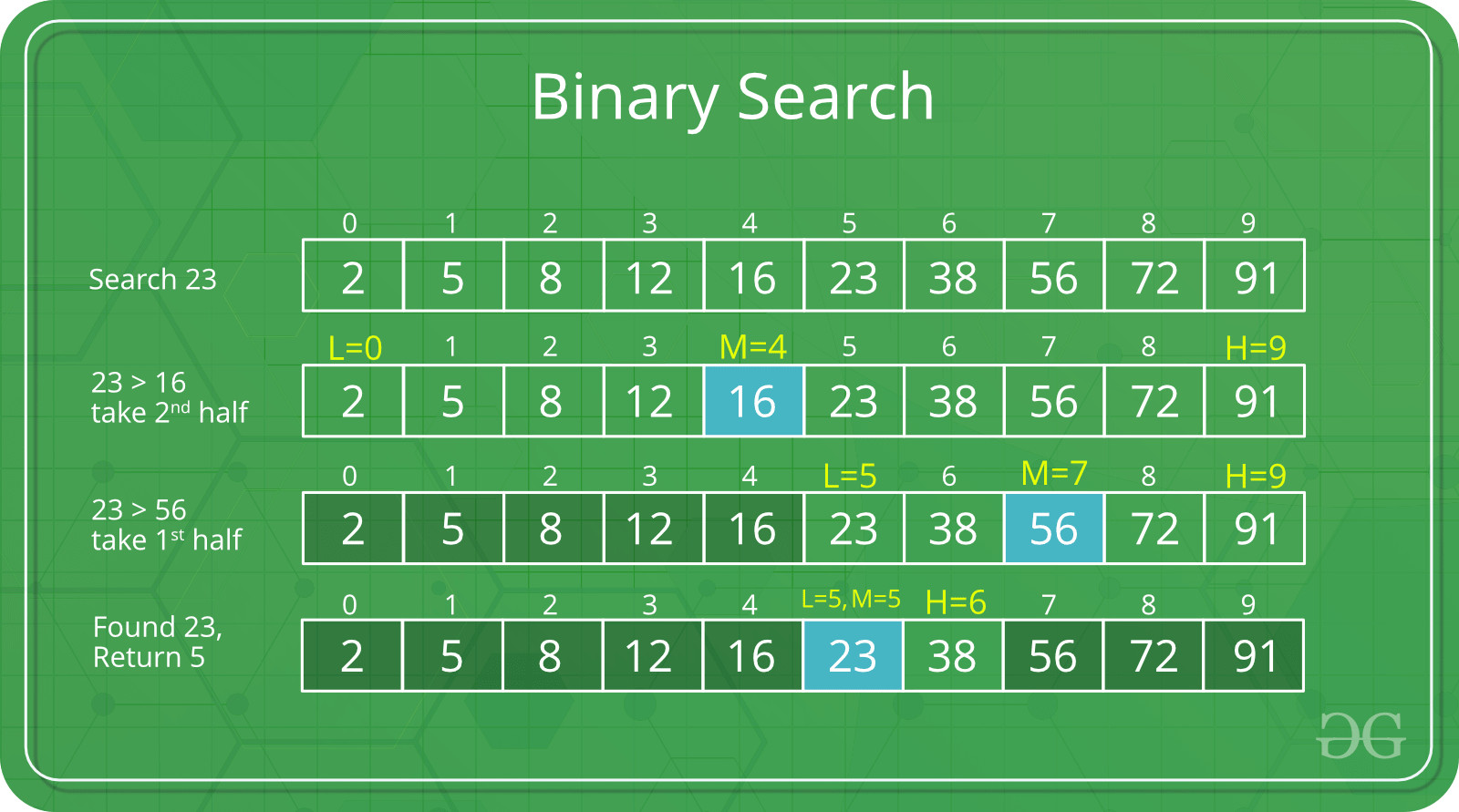
二分查找的思想是利用数组排序的信息,将时间复杂度降低到O(Log n)。
搜索算法旨在检查元素或从存储元素的任何数据结构中检索元素。根据搜索操作的类型,这些算法一般分为两类:
难度级别: 基本
最后更新: 2021 年 6 月 28 日
问题:给定一个包含 n 个元素的数组 arr[],编写一个函数来搜索 arr[] 中的给定元素 x。
例子 :
输入: arr[] = {10, 20, 80, 30, 60, 50,
110, 100, 130, 170}
x = 110;
输出: 6
元素 x 出现在索引 6
输入: arr[] = {10, 20, 80, 30, 60, 50,
110, 100, 130, 170}
x = 175;
输出: -1
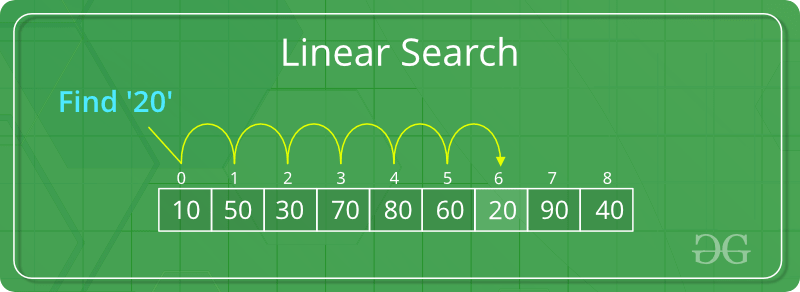
元素 x 不存在于 arr[] 中。一种简单的方法是进行线性搜索,即
从 arr[] 最左边的元素开始,将 x 与 arr[] 的每个元素一一比较
如果 x 与元素匹配,则返回索引。
如果 x 与任何元素都不匹配,则返回 -1。
<script>
// Javascript code to linearly search x in arr[]. If x
// is present then return its location, otherwise
// return -1
function search(arr, n, x)
{
let i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ];
let x = 10;
let n = arr.length;
// Function call
let result = search(arr, n, x);
(result == -1)
? document.write("Element is not present in array")
: document.write("Element is present at index " + result);
// This code is contributed by Manoj
</script>上述算法的时间复杂度为 O(n)。
线性搜索在实际中很少使用,因为其他搜索算法(例如二分搜索算法和哈希表)与线性搜索相比可以显着加快搜索速度。
提高线性搜索最坏情况的复杂性
下面是实现:
<script>
// Javascript program for linear search
function search(arr, search_Element)
{
let left = 0;
let length = arr.length;
let right = length - 1;
let position = -1;
// Run loop from 0 to right
for(left = 0; left <= right;)
{
// If search_element is found
// with left variable
if (arr[left] == search_Element)
{
position = left;
document.write(
"Element found in Array at " +
(position + 1) + " Position with " +
(left + 1) + " Attempt");
break;
}
// If search_element is found
// with right variable
if (arr[right] == search_Element)
{
position = right;
document.write(
"Element found in Array at " +
(position + 1) + " Position with " +
(length - right) + " Attempt");
break;
}
left++;
right--;
}
// If element not found
if (position == -1)
document.write("Not found in Array with " +
left + " Attempt");
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
let search_element = 5;
// Function call
search(arr, search_element);
// This code is contributed by code_hunt
</script>在第 5 个位置的 Array 中找到了 1 次尝试的元素
给定一个由 n 个元素组成的排序数组 arr[],编写一个函数来搜索 arr[] 中的给定元素 x。
一种简单的方法是进行线性搜索。上述算法的时间复杂度为 O(n)。执行相同任务的另一种方法是使用二分搜索。
二分搜索:通过重复将搜索间隔分成两半来搜索已排序的数组。从覆盖整个阵列的区间开始。如果搜索关键字的值小于区间中间的项,则将区间缩小到下半部分。否则,将其缩小到上半部分。反复检查直到找到值或间隔为空。
例子 :

二分查找的思想是利用数组排序的信息,将时间复杂度降低到O(Log n)。
在一次比较之后,我们基本上忽略了一半的元素。
二分查找的递归实现
<script>
// JavaScript program to implement recursive Binary Search
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
function binarySearch(arr, l, r, x){
if (r >= l) {
let mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ];
let x = 10;
let n = arr.length
let result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? document.write( "Element is not present in array")
: document.write("Element is present at index " +result);
</script>在这里您可以创建一个检查功能,以便于实现。
这是带有检查功能的递归实现,我觉得这是一个更简单的实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//define array globally
const int N = 1e6 +4;
int a[N];
int n;//array size
//elememt to be searched in array
int k;
bool check(int dig)
{
//element at dig position in array
int ele=a[dig];
//if k is less than
//element at dig position
//then we need to bring our higher ending to dig
//and then continue further
if(k<=ele)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void binsrch(int lo,int hi)
{
while(lo<hi)
{
int mid=(lo+hi)/2;
if(check(mid))
{
hi=mid;
}
else
{
lo=mid+1;
}
}
//if a[lo] is k
if(a[lo]==k)
cout<<"Element found at index "<<lo;// 0 based indexing
else
cout<<"Element doesnt exist in array";//element was not in our array
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
cin>>k;
//it is being given array is sorted
//if not then we have to sort it
//minimum possible point where our k can be is starting index
//so lo=0
//also k cannot be outside of array so end point
//hi=n
binsrch(0,n);
return 0;
}二分查找的迭代实现
<script>
// Program to implement recursive Binary Search
// A recursive binary search function. It returns
// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
function binarySearch(arr, l, r, x)
{
if (r >= l) {
mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
// If the element is present at the middle
// itself
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
// If element is smaller than mid, then
// it can only be present in left subarray
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
// We reach here when element is not
// present in array
return -1;
}
arr =new Array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);
x = 10;
n = arr.length;
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1) ? document.write("Element is not present in array")
: document.write ("Element is present at index " + result);
// This code is contributed by simranarora5sos
</script>时间复杂度:
二分查找的时间复杂度可以写成
T(n) = T(n/2) + c